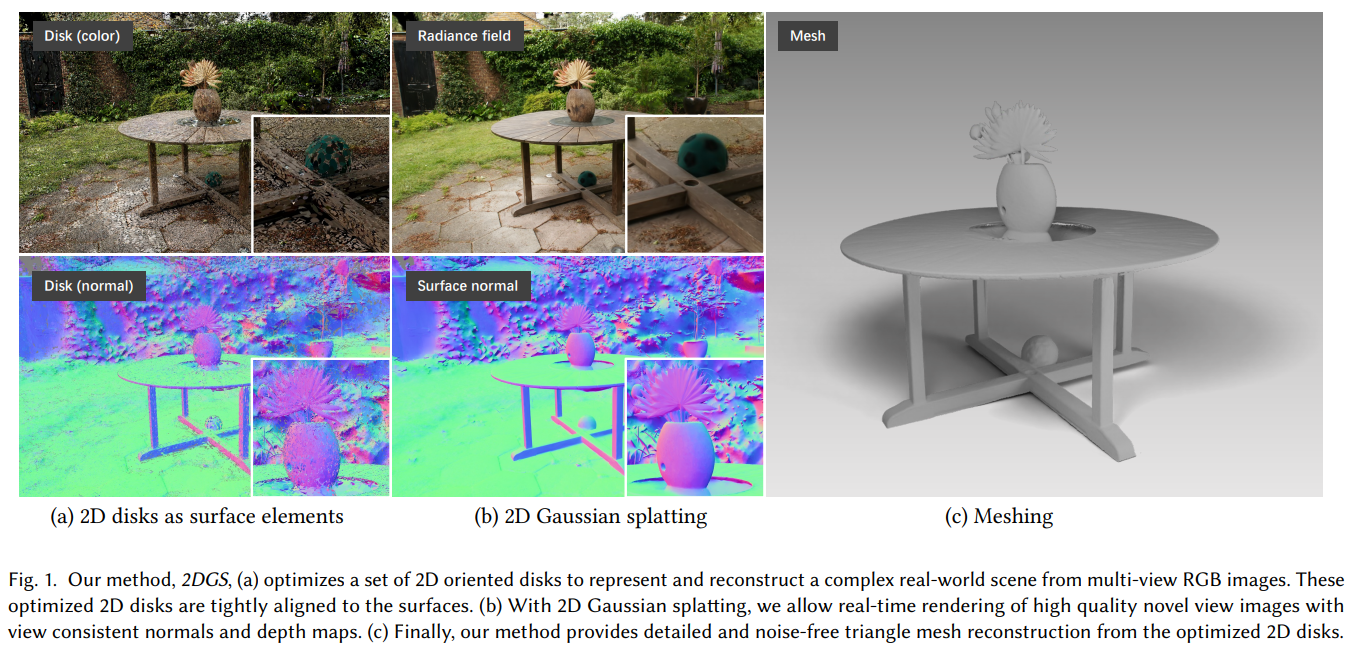
2DGS
https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.17888
https://surfsplatting.github.io/
Mesh生成器: 3D 高斯可能因为体积过大而模糊,深度不一致
Primitive
- Unlike 3DGS [Kerbl et al. 2023], which models the entire angular radiance in a blob, we simplify the 3-dimensional modeling by adopting “flat” 2D Gaussians embedded in 3D space.
- With 2D Gaussian modeling, the primitive distributes densities within a planar disk, defining the normal as the direction of the steepest change of density. (法线垂直于2D盘)
- By skipping the third row and column of \(\Sigma'\), we obtain a 2D Gaussian \(G_{2D}\) with covariance matrix \(\Sigma_{2D}\).
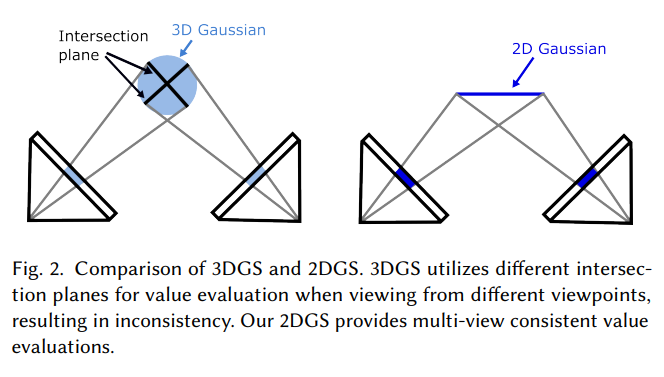
3D Space
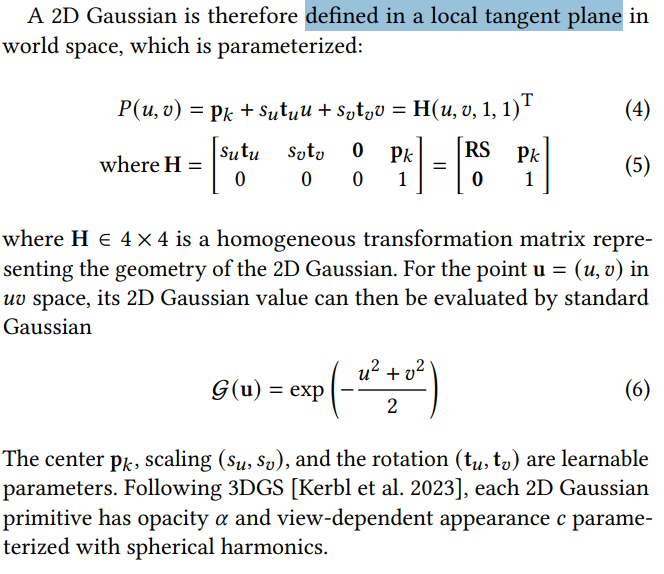
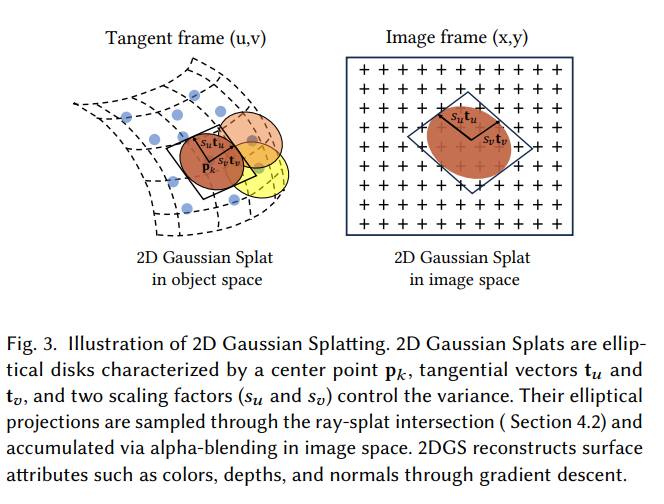
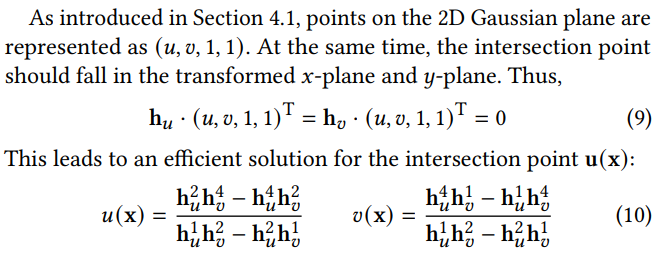
- Its central point is $p_k$,
- Two principal tangential vectors \(t_u\) and \(t_v\)
- A scaling vector \(S = (s_u, s_v)\) that controls the variances of the 2D Gaussian.
- The primitive normal: \(t_w = t_u \times t_v\).
- The orientation: \(3 \times 3\) rotation matrix \(R = [t_u, t_v, t_w]\),
- The scaling factors: \(3 \times 3\) diagonal matrix: \(S = \begin{bmatrix} s_u & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & s_v & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}\)
- P(u,v) : 平面上某个点在世界坐标系的位置
Splatting
\[x = (xz, yz, z, z)^{\top} = W P(u,v) = W H(u, v, 1, 1)^{\top}.\]- x is ray emitted from the camera and passing through pixel (𝑥, 𝑦) and intersecting the splat at depth 𝑧.
- \(M = {(WH)}^{-1}\) : project its conic into the screen space with an implicit method
- 普通仿射 → 只保证椭圆中心点在对的位置,边缘可能扭曲
- implicit conic → 用一个方程描述整个椭圆在相机平面上的位置和形状,保证整体投影准确
问题:Inverse transformation introduces numerical instability
特别是当当 splat 从侧面看几乎退化成线时,逆矩阵求射线交点可能不是确定解(无数交点)
解决:Ray-splat Intersection
- 每个像素坐标 x=(x,y) 对应一个射线
- 将这个射线表示为两个正交平面的交线
- 平面变换到高斯局部坐标

- 求交点
问题:特殊pose
When a 2D Gaussian is observed from a slanted viewpoint, it degenerates to a line in screen space. Therefore, it might be missed during rasterization.
To deal with these cases and stabilize optimization
解决:Degenerate Solutions
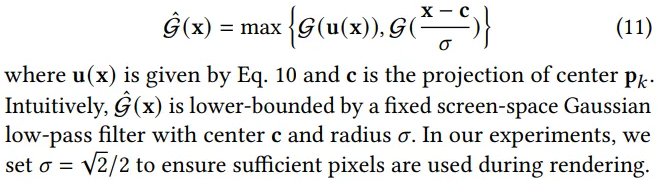
加一个 固定屏幕空间半径的低通高斯滤波 → 保证每个退化 splat 仍然有贡献 → 优化稳定
给贡献不突出的点强行加一点影响值, 以中心 c 为圆心,半径 σ 的高斯保底
这样 rasterization 不会漏掉 splat → 梯度稳定 → 可微分渲染可靠
Rasterization
没啥好说的
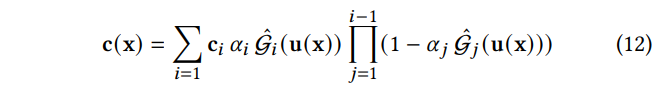
训练:额外加了两个Term
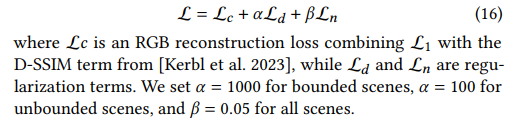
Normal Consistency
让每个 splat 的法向量和真实物体表面法向量 尽量一致
- \(n_i\) represents the normal of the splat that is oriented towards the camera
- 𝜔 denotes the blending weight of the intersection point
- N is the normal estimated by the gradient of the depth map
- 沿射线累积透明度到 0.5 的点 作为表面点 $p_s$
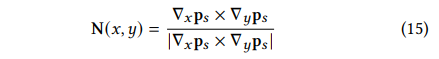
Depth Distortion
encourages the concentration of the splats
- concentrates 2D primitives distributed within a tight range along the ray, addressing the rendering process’s limitation where the distance between Gaussians is ignored.
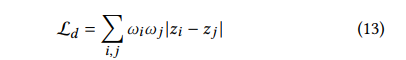
- \(𝜔\) denotes the blending weight of the intersection point
- \(𝑧_𝑖\) is the depth of the intersection points
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: