Modeling (2) — Surface Reconstruction
Reference: https://www.cs.sfu.ca/~haoz/teaching/cmpt464/index.html SFU CMPT 464 Computer Graphics Course Notes by Hao Zhang 学习笔记 可能有理解错的地方,不保真!!!
Classical Surface Reconstruction
Occupancy
\(o(\mathbf{x}) = \begin{cases} 1, & \mathbf{x} \text{ 在物体内部} \\ 0, & \mathbf{x} \text{ 在物体外部} \end{cases}\) \(o(\mathbf{x}) \in [0, 1], \quad o(\mathbf{x}) = \text{概率}(\mathbf{x} \text{ 在物体内部})\)
- 中间值表示不确定性(例如学习到的 Occupancy 网络输出)
- 不提供距离信息,只有几何边界的位置。
- 通常用于体素网格(Voxel Grid)表示或者隐式 3D 网络(Occupancy Networks)
- 用 Marching Cubes 或类似算法,把占据概率 0.5 作为阈值提取网格。
3DCNN (Auto-Encoding 3D Shapes)
- 输入是体素化后的三维形状,也就是一个三维张量 \(V \in \{0,1\}^{64\times64\times64}\)
- 每个体素 (voxel) 表示空间中一个立方体单元是否被物体占据;
- 1 = 物体内部,0 = 空气;
- 相当于一个 3D 二值图像。
- 输出就是从 64³ 的体素体积中提取全局形状语义特征,压缩成 128 维潜向量 z
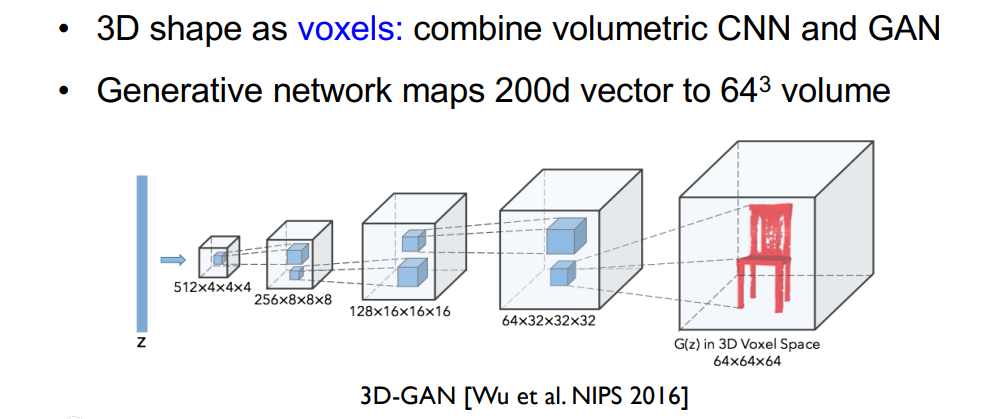
3D-GAN (3D Generative Adversarial Network)
| 输入 | 随机向量 z ∈ ℝ²⁰⁰(高斯或均匀分布) |
|---|---|
| 输出 | 三维体素网格 \(V ∈ [0,1]^{64\times64\times64}\)(表示占据概率) |
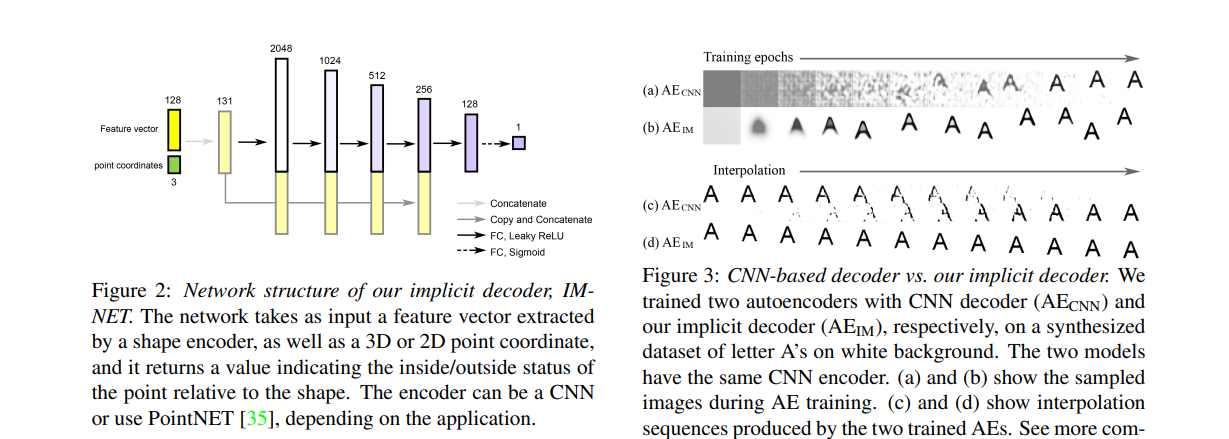
IM-NET: Learning Implicit Fields for Generative Shape Modeling
Signed Distance Function (SDF)
Distance from a point p to a surface M is the distance from p to a closest point on M
- SDF公式: \(f (p) = (p - o_i ) \times n_i\)
- \(o_i\) 作为切平面中心
- is closest to p
- p 空间中的任意点(query point)
- Signed f(p) 离曲面多远,在内还是外 is signed distance from p to “closest tangent plane”
- \(o_i\) 作为切平面中心
点云切平面
- 曲面未知:由于真实曲面 M 不知道,根据点云中的扫描到的采样点→估计切平面近似曲面
- \(Nbr(x_i, k)\) = the set of k nearest neighbors (kNN) of a data
- \(x_i\) → 云中的扫描到的采样点(已知)
- Center \(o_i\) is the centroid of \(Nbr(x_i, k)\)
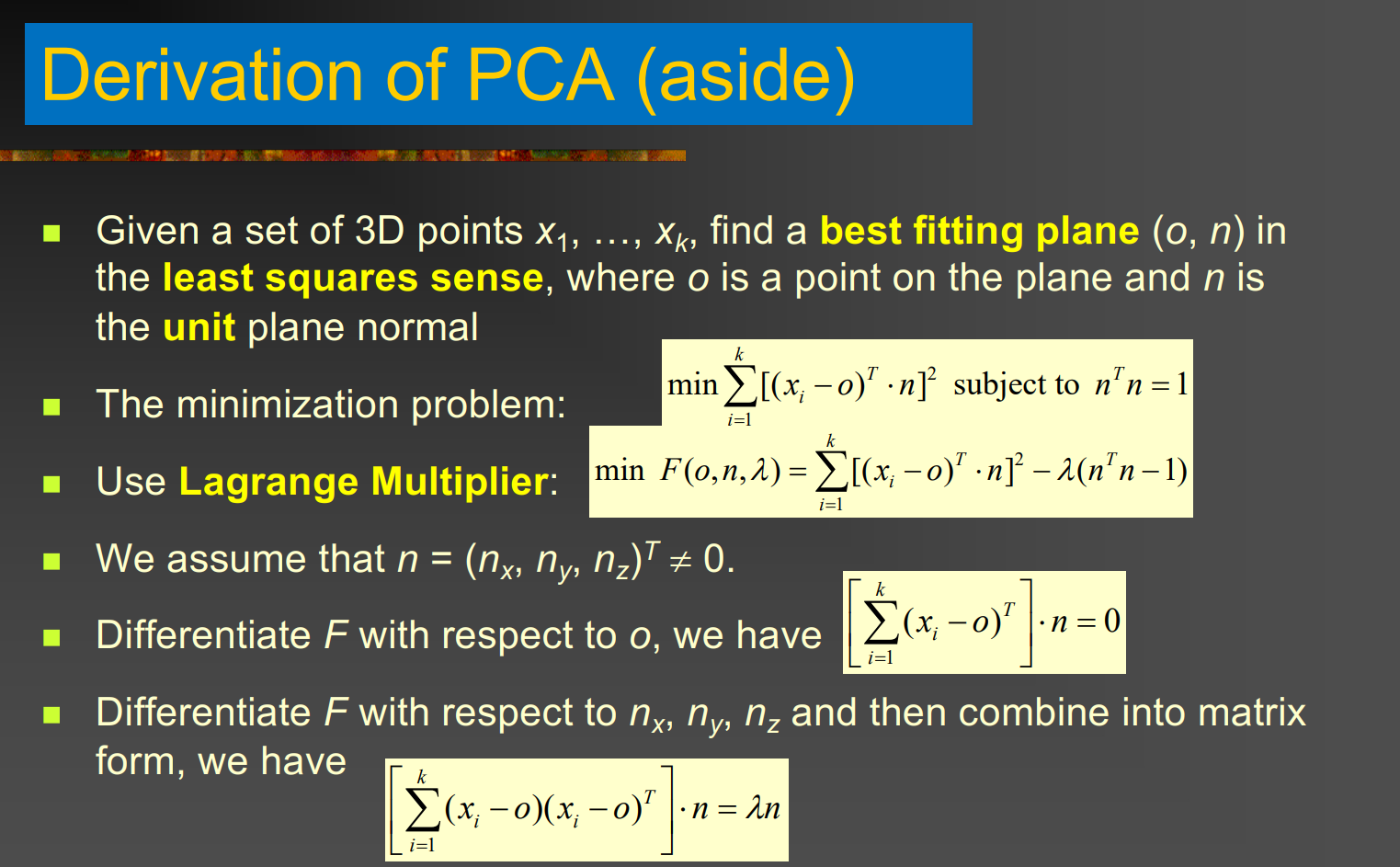
- Normal \(n_i\) is determined by principal component analysis (PCA)
- 邻域点的协方差矩阵: \(C_i = \frac{1}{k} \sum_{x_j \in N_i} (x_j - \bar{x}_i)(x_j - \bar{x}_i)^T\)
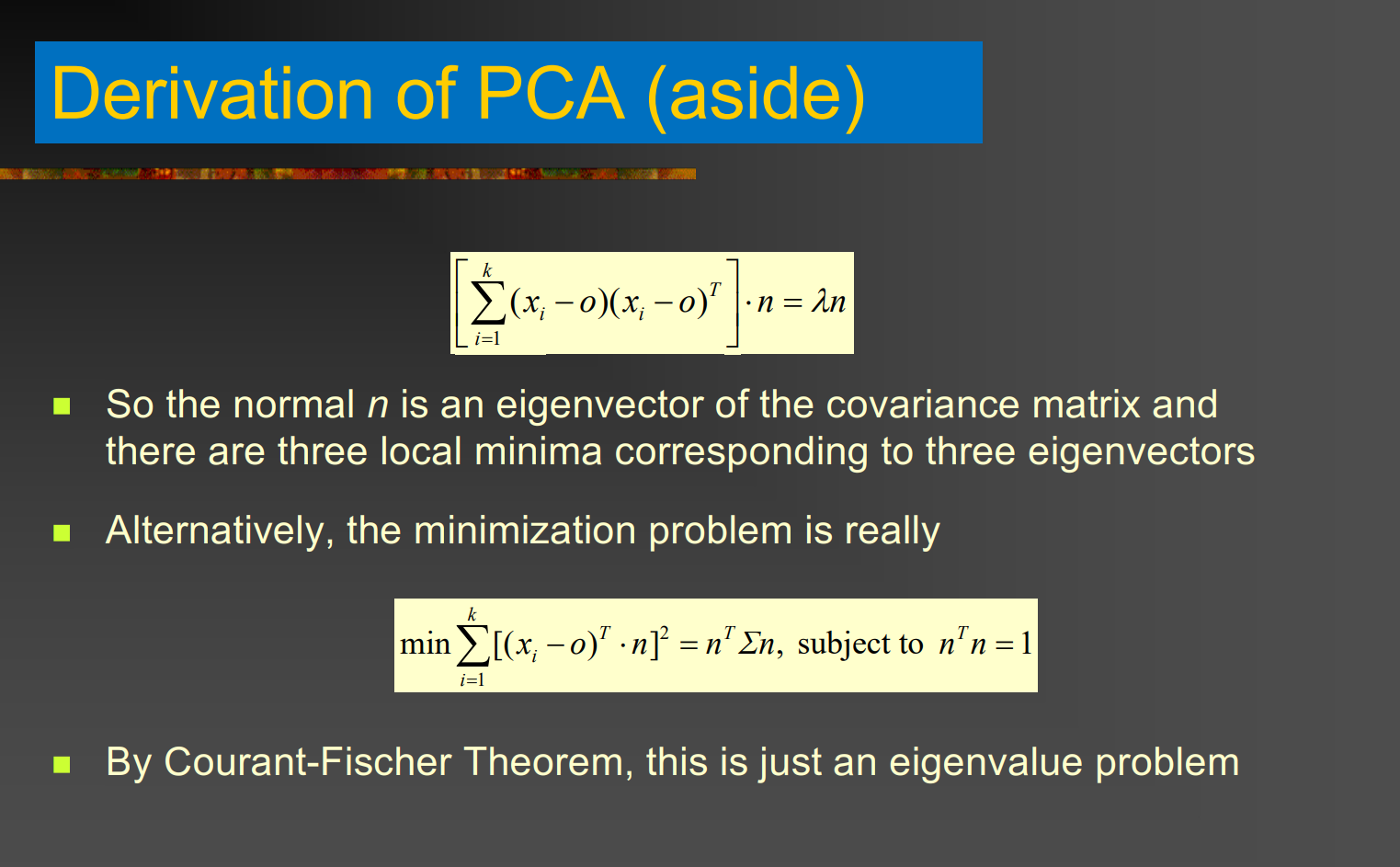
- PCA 特征分解: \(C_i v_l = \lambda_l v_l, \quad l=1,2,3, \quad \lambda_1 \ge \lambda_2 \ge \lambda_3\)
- 法线 \(n_i\) = 最小特征值对应的特征向量: \(n_i = v_3\)
- 构建切平面: \(f_i(p) = n_i \cdot (p - o_i), \quad o_i = x_i\)
- 满足:\(\min_{n_i} \sum_{x_j \in N_i} (n_i \cdot (x_j - o_i))^2\)
- PCA 本质上就是做最小二乘拟合,只不过通过特征分解得到解而不是显式求解最小二乘方程,不是新的计算步骤。
- 满足:\(\min_{n_i} \sum_{x_j \in N_i} (n_i \cdot (x_j - o_i))^2\)
- \(Nbr(x_i, k)\) = the set of k nearest neighbors (kNN) of a data
点云或曲面重建中法线一致性(consistent normal orientation)的问题
如果某些点的法线朝内,某些朝外,整体曲面会“翻转” → 把这个问题建模为图优化问题
Riemannian graph
- 节点:每个切平面中心 $o_i$
- EMST(Euclidean Minimum Spanning Tree,欧几里得最小生成树)
- EMST只提供 n-1 条边,局部邻居信息不够丰富,无法完整表示点云的几何结构
- 增加局部邻居边: Add an edge \((N_i, N_j)\) to EMST if \(o_i\) is one of the k closest neighbors of \(o_j\) or vice versa
- Cost of edge \((N_i, N_j)\) is \(n_i \times n_j\) (maximum if coplanar)
- Find orientation to maximize the total cost in graph
- Propagation
- 从某个切平面(tangent plane)开始
- Traversing the Riemannian graph
- 优先沿曲率小的方向传播 \(\kappa_{ij}=\arccos(n_i \cdot n_j)\) 越小 → 两平面几乎平行 → 优先传播
- 对当前节点\(N_i\),找所有邻居\(N_j\)
- 如果未确定方向:
- 计算 dot product
- dot < 0 → 翻转
- 标记已确定
- 把 \(N_j\) 加入队列,等待传播
- 如果未确定方向:
- 重复直到队列为空

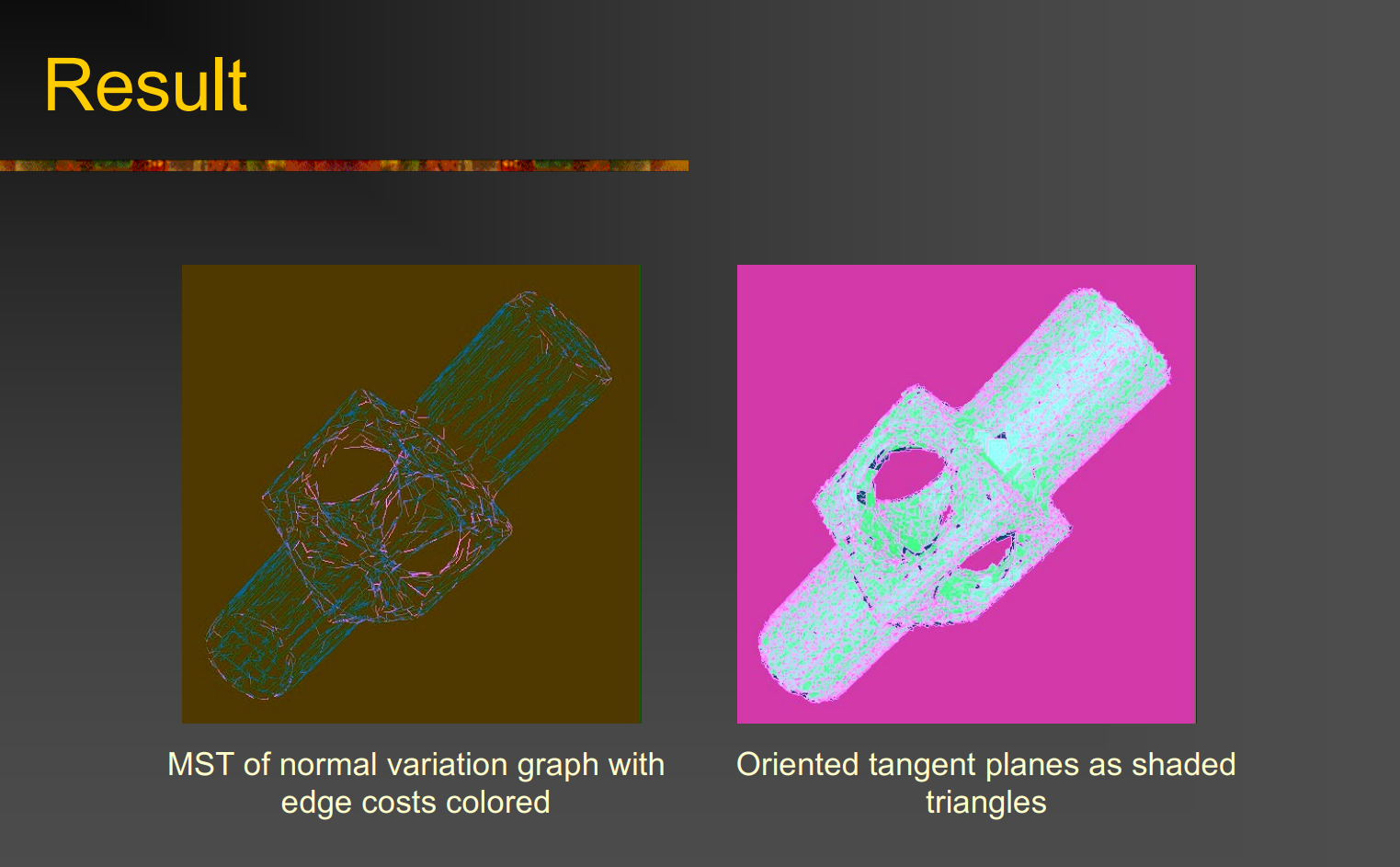
Surface Reconstruction from Unorganized Points
目的:如何从一堆没有顺序、没有拓扑信息的点云中重建出一个平滑、连续的曲面(surface)
困难:
- 一组三维点 \(P = \{p_i\}\),比如从激光扫描、深度相机采样得到
- 这些点 无序(unorganized),也 没有面、边、法线信息
- 我们希望恢复出一个连续、光滑的曲面 S,尽可能贴合这些点。
核心思想:
- 曲面定义为一个隐式函数的等值面: \(S=\{x∈R^3∣f(x)=0\}\)
- Assumptions(算法成立的前提)
- 每个点\(x_i\)距离真实曲面上的对应点不超过距离 \(d\)
- 曲面 \(M\) 上任意一点为中心,半径 \(r\) 的球中至少有一个采样点 → 算法无法区分那是曲面上的空洞(真孔)还是采样缺失(假空)
-
Hole condition: 如果在采样点云中存在一个球体,半径 = \((d + r)\),内部没有任何点 → 被认为是真实结构中的洞 Overview of Hoppe’s approach
- Step 1: 构建隐式函数 f: SDF(Signed Distance Function)
- Step 2: Contouring / Marching Cubes 算法 approximates zero-set Z(f ) of f by a triangle mesh
点云切平面生成曲面(iso-surface)
- 已经有了带方向的切平面 → 计算 SDF
- 提取零等值面 用 Marching Cubes (Contour tracing(轮廓提取))
- Preparation for cubes marching
- 将三维空间划分成立方体网格(cubic grids)
- 在每个立方体的八个顶点计算 SDF(Signed Distance Function)值
- 只处理 零等值面穿过的立方体 → 立方体顶点存在正值和负值 → 零交点必穿过
- 如果立方体某个顶点的 SDF 未定义(没有有效的距离信息),则该立方体无法与零等值面交叉 → 可以跳过
- Size of cube » d + r (前面的Assumptions)
- Marching Cubes
- 逐个立方体处理
- 检查顶点标量值
- 每个顶点的标量值是正或负 → 得到 8 位二进制编码(0~255)。
- 查表 → 预定义三角形生成规则
- 利用对称性 → 只需要 15 种基本模式,其他模式通过旋转/镜像生成
-
例如:零等值面穿过 edge0, edge3, edge8 → 生成一个三角形
case 3: // 二进制编码 00000011 triangles = [(edge0, edge3, edge8)]
- 计算边交点 → 生成三角形
- 每条立方体边连接两个顶点 $v_1$ 和 $v_2$,对应标量值为 \(f(v_1)\) 和 \(f(v_2)\)。如果 \(f(v_1)\) 和 \(f(v_2)\) 符号不同,则零等值面穿过该边,交点坐标通过线性插值得到:
- \[P_{\text{intersect}} = v_1 + \frac{0 - f(v_1)}{f(v_2) - f(v_1)} (v_2 - v_1)\]
- 3 个交点 → 一个三角形
- 6 个交点 → 两个三角形
- 每条立方体边连接两个顶点 $v_1$ 和 $v_2$,对应标量值为 \(f(v_1)\) 和 \(f(v_2)\)。如果 \(f(v_1)\) 和 \(f(v_2)\) 符号不同,则零等值面穿过该边,交点坐标通过线性插值得到:
- Preparation for cubes marching
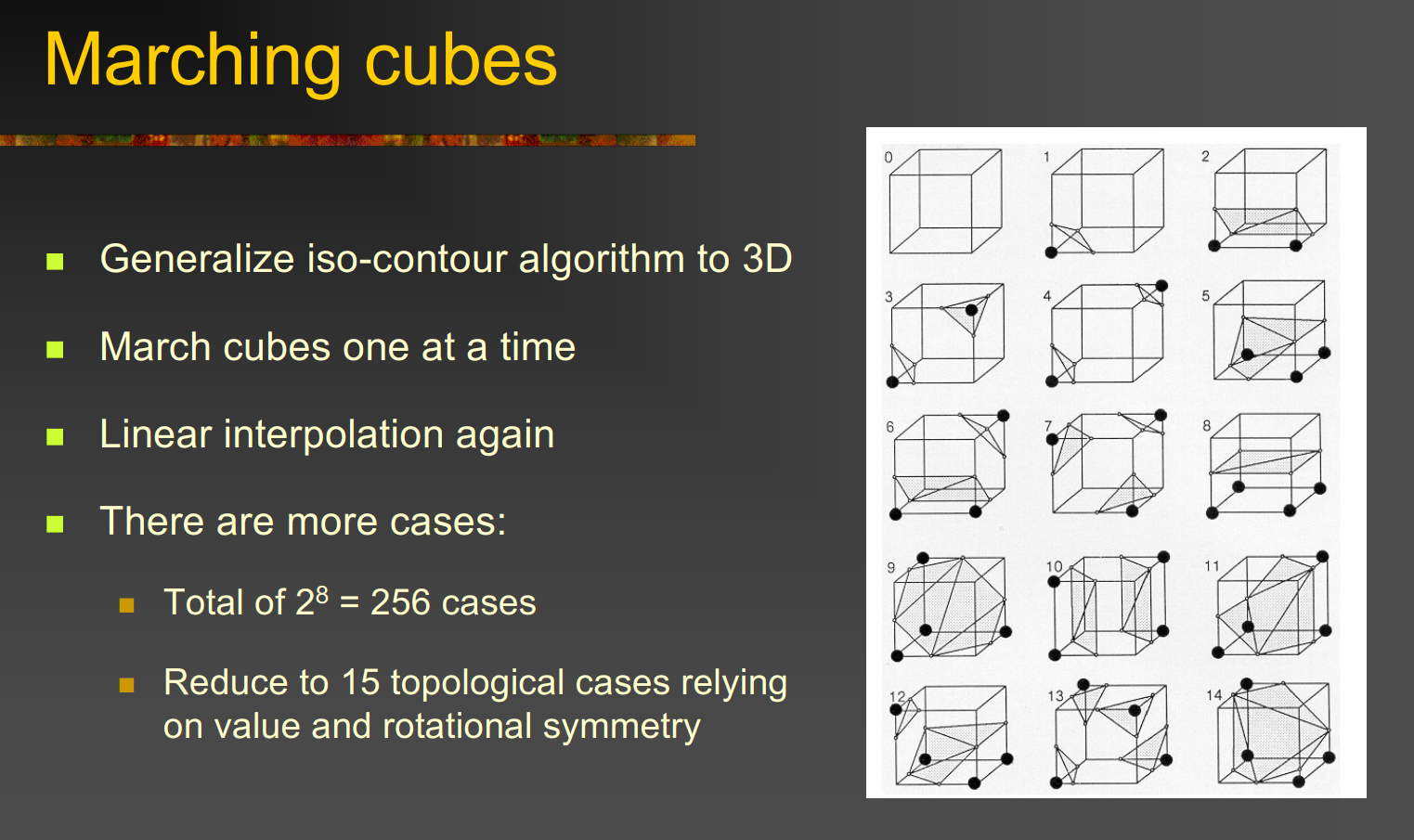
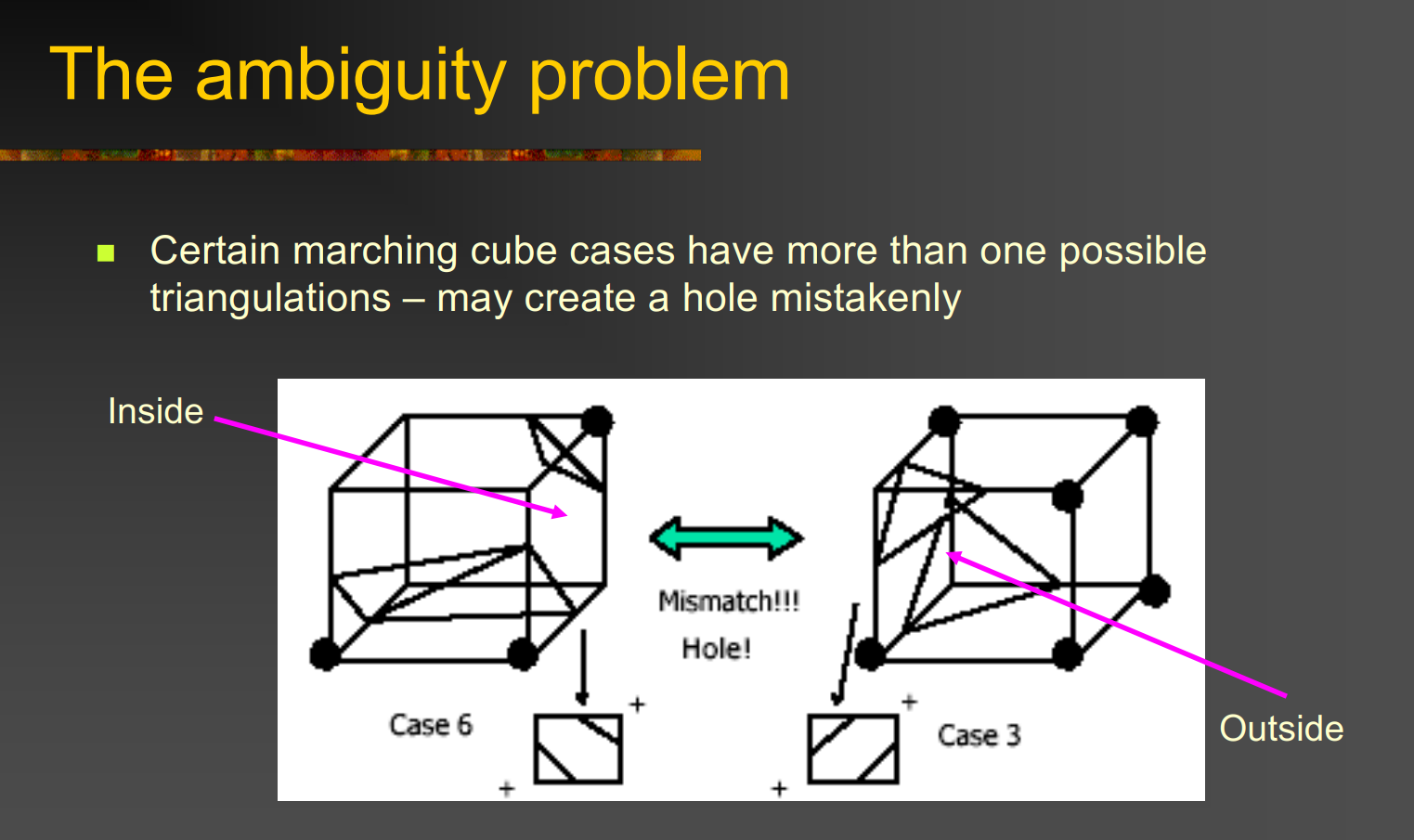
具体计算
https://iquilezles.org/articles/distfunctions/
def determine_sphere_sdf(query_points, sphere_params):
"""Query sphere sdf for a set of points.
Args:
query_points (torch.tensor): Nx3 tensor of query points.
sphere_params (torch.tensor): Kx4 tensor of sphere parameters (center and radius).
Returns:
torch.tensor: Signed distance field of each sphere primitive with respect to each query point. NxK tensor.
"""
# Determine the SDF value of each query point with respect to each sphere, you may reuse the function from task 3 with modifications
sphere_params = sphere_params.unsqueeze(0)
centers = sphere_params[:, :3]
radii = sphere_params[:, 3]
diff = query_points[:, None, :] - centers[None, :, :] # (N, K, 3)
dist = torch.linalg.norm(diff, dim=2) # (N, K)
sphere_sdf = dist - radii[None, :]
return sphere_sdf
def determine_box_sdf(query_points, box_params):
"""Query box SDF for a set of points.
Args:
query_points (torch.tensor): Nx3 tensor of query points.
box_params (torch.tensor): 6 tensor of box parameters (center and half-extents).
Returns:
torch.tensor: SDF field of box primitive with respect to each query point.
"""
# Use half-extents to determine the box boundaries
box_params = box_params.unsqueeze(0)
center = box_params[:, :3]
half_extents = box_params[:, 3:
p_local = query_points - center
q = torch.abs(p_local) - half_extents
outside_dist = torch.norm(torch.clamp(q, min=0.0), dim=1)
inside_dist = torch.min(torch.max(q, dim=1).values, torch.tensor(0.0, device=query_points.device))
box_sdf = outside_dist + inside_dist
return box_sdf.unsqueeze(1)
def determine_torus_sdf(query_points, torus_params):
"""Query torus SDF for a set of points.
Args:
query_points (torch.tensor): Nx3 tensor of query points.
torus_params (torch.tensor): 5 tensor of torus parameters (center, major_radius, minor_radius).
Returns:
torch.tensor: SDF field of torus primitive with respect to each query point.
"""
# Major radius is the distance from center to the ring center
# Minor radius is the thickness of the ring
torus_params = torus_params.unsqueeze(0)
center = torus_params[:, :3]
major_radius = torus_params[:, 3]
minor_radius = torus_params[:, 4]
p = query_points - center
q_x = torch.norm(p[:, [0, 2]], dim=1) - major_radius
q_y = p[:, 1]
torus_sdf = torch.sqrt(q_x**2 + q_y**2) - minor_radius
return torus_sdf.unsqueeze(1)
Occupancy vs SDF
| 特性 | Occupancy | SDF |
|---|---|---|
| 输出类型 | 二值或概率 | 连续距离(正/负) |
| 内外信息 | 是 | 是 |
| 距离信息 | 否 | 是 |
| 表面表示 | 隐式通过阈值提取 | 直接通过零水平面 |
| 法向量计算 | 需要额外估计 | 可直接通过梯度计算 |
| 训练复杂度 | 简单 | 中等,需要距离监督 |
| 用例 | Occupancy Networks, Voxel Grids | DeepSDF, NeuS, Signed Distance-based Reconstruction |
实际项目中:
- SDF 更适合神经隐式表示(NeRF-like 或 DeepSDF)
- Occupancy网络更适合快速体素化或者多物体场景
- Occupancy → 二值或概率输出 → BCE很稳定, 容易训练, 不需要复杂的连续距离监督
Constructed solid geometry (CSG)
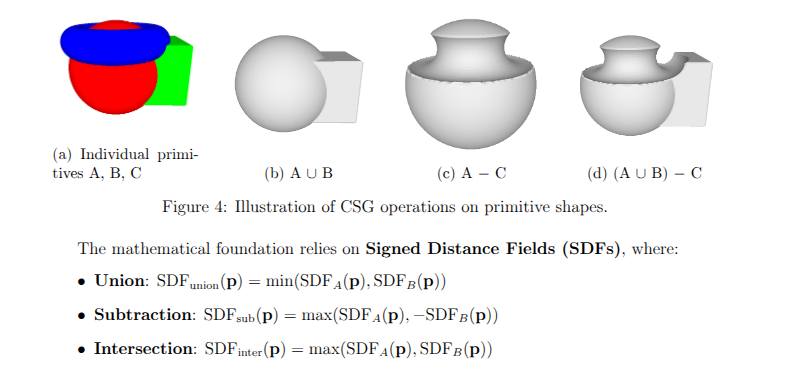
def csg_union(sdf1, sdf2):
"""Perform CSG union operation (minimum of two SDFs).
Args:
sdf1 (torch.tensor): SDF values for first shape
sdf2 (torch.tensor): SDF values for second shape
Returns:
torch.tensor: Union SDF values
"""
# Implement CSG union operation
union_sdf = torch.min(sdf1, sdf2)
return union_sdf
def csg_subtraction(sdf1, sdf2):
"""Perform CSG subtraction operation (sdf1 - sdf2).
Args:
sdf1 (torch.tensor): SDF values for shape to subtract from
sdf2 (torch.tensor): SDF values for shape to subtract
Returns:
torch.tensor: Subtraction SDF values
"""
# Implement CSG subtraction operation
subtraction_sdf = torch.max(sdf1, -sdf2)
return subtraction_sdf
Neural Surface Reconstruction
IM-NET: Learning Implicit Fields for Generative Shape Modeling
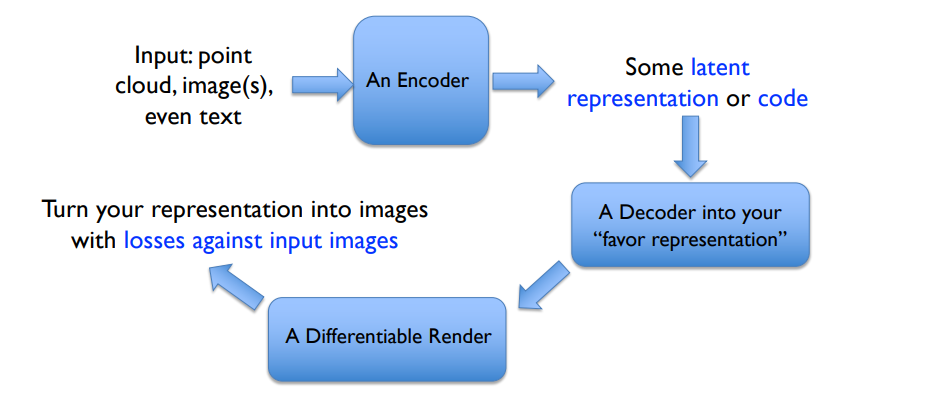
输入:
- 3D 坐标 x
- 可选 latent vector z(用于生成特定类别或特定形状)(encoder得到)
输出: 该点是否在物体内部(occupancy)
生成阶段:从隐式场到 mesh
- 采样网格(Voxel Grid)
- 将三维空间划分为小立方体(cube)。
- 每个立方体由 8 个顶点组成,每个顶点有对应的 occupancy 值 \(v_i = f_\theta(x_i)\)
- 判断顶点符号
- 给定阈值 t(通常 0.5),标记每个顶点是 inside(\(v_i \ge t\))还是 outside(\(v_i < t\))。
- 8 个顶点 → 2⁸ = 256 种可能的 inside/outside 组合。
- 查表生成三角形
- 对每种组合,Marching Cubes 预先定义好的三角形表(triangle table)
- 对称性和旋转可以把 256 种组合简化为 15 种基本模式。
- 插值确定顶点位置
- 三角形顶点通常在立方体边上,利用 线性插值 计算:
- \[\mathbf{p} = \mathbf{p}_1 + \frac{t - v_1}{v_2 - v_1} (\mathbf{p}_2 - \mathbf{p}_1)\]
- \(p_1, p_2\) 是边的两个端点,\(v_1,v_2\) 是对应的 occupancy 值
- 三角形顶点通常在立方体边上,利用 线性插值 计算:
- 生成三角形网格
Cube: 8 vertices, values v0..v7
Values > t: inside, < t: outside
v7 -------- v6
/ | / |
v3 -------- v2 |
| | | |
| v4 -------| v5
|/ |/
v0 -------- v1
根据 vertex 的 inside/outside 状态,查表生成 1~5 个三角形
插值计算三角形顶点位置
发展
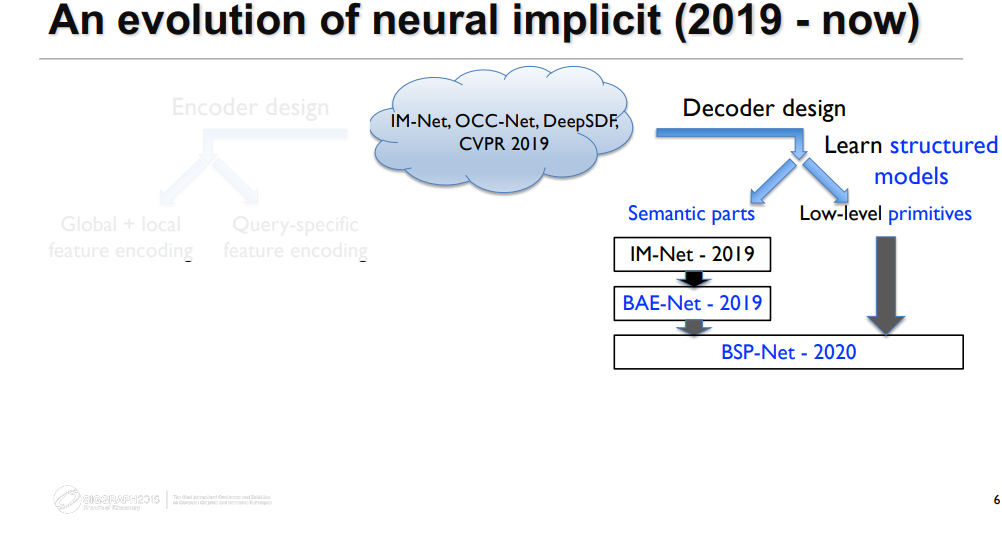
Base on IM-Net [Chen and Zhang, CVPR 2019] 奠基之作
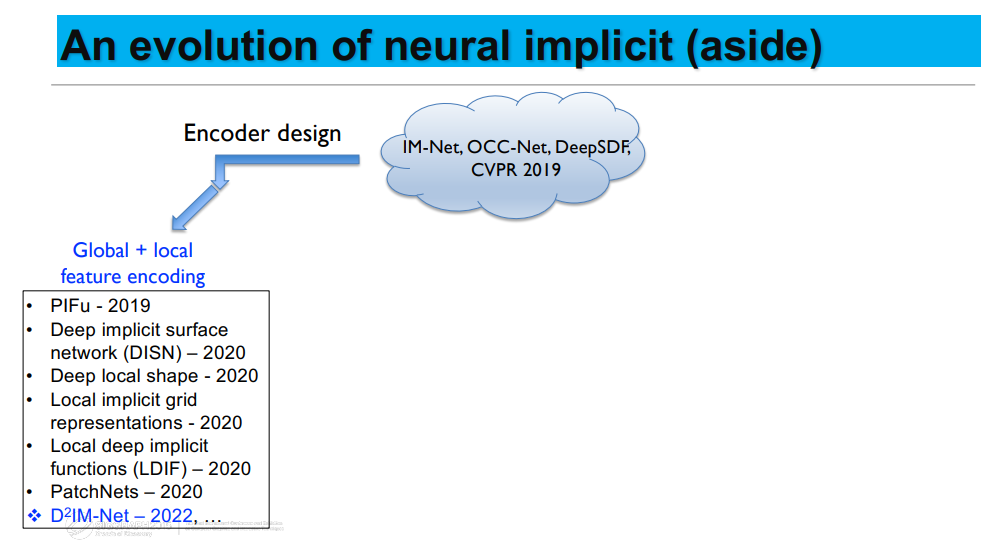
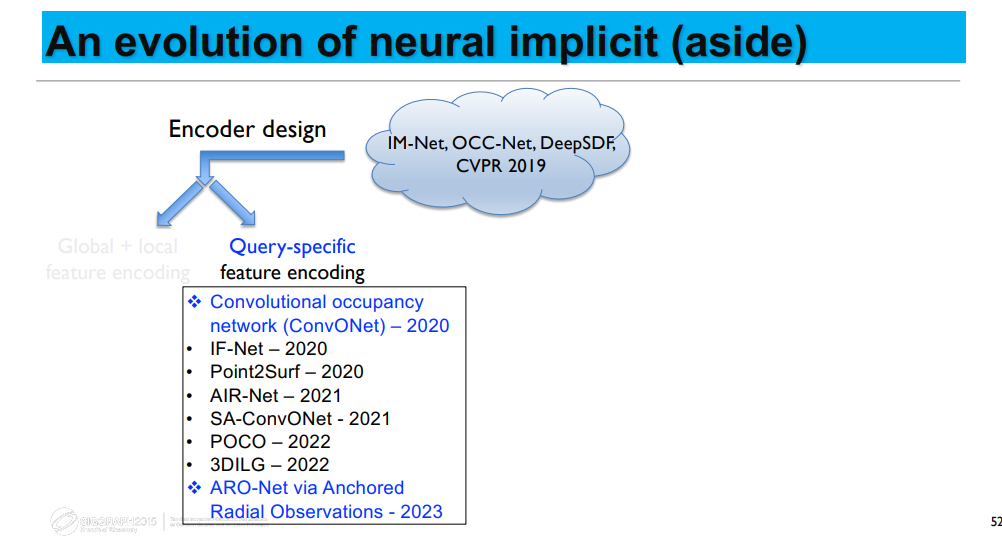
Encoder Design

Decoder Design
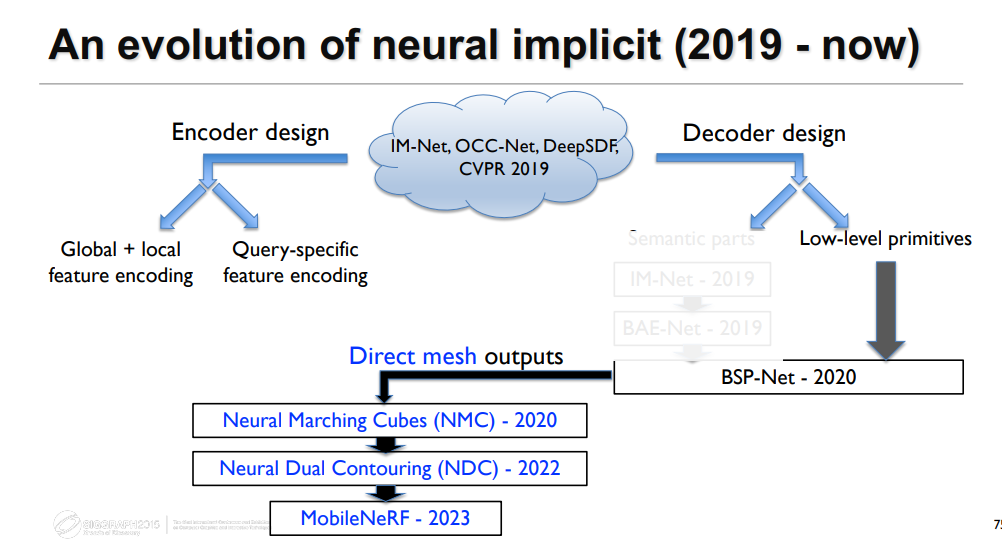
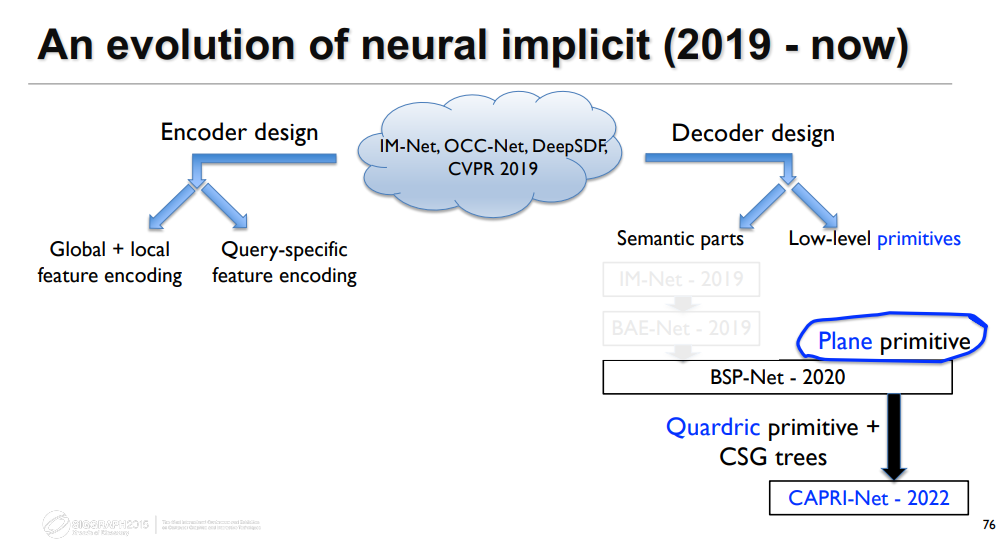
Mesh Decimation
依赖于拓扑信息
假设网格是“连通的”,即顶点和面之间有明确邻接关系
Quadric Error Metrics (QEM)
- 初始化 Quadri
- 对网格每个面 f 计算平面方程:ax + by + cz + d = 0
- 计算面 quadric:\(Q_f = \begin{bmatrix} a^2 & ab & ac & ad\\ ab & b^2 & bc & bd\\ ac & bc & c^2 & cd\\ ad & bd & cd & d^2 \end{bmatrix}\)
- 对每个顶点 v 累加邻接面的 quadric:\(Q_v = \sum_{f \in \text{adj}(v)} Q_f\)
- 对网格每个面 f 计算平面方程:ax + by + cz + d = 0
- 计算边折叠误差
- 对每条边 \((v_1, v_2)\) \(Q_{\text{edge}} = Q_{v_1} + Q_{v_2}\)
- 构建误差函数:\(\text{Error}(v_{\text{new}}) = v_{\text{new}}^T Q_{\text{edge}} v_{\text{new}}\)
- 最优顶点 \(v_{\text{new}}\) 由线性系统求解:\(\begin{bmatrix} q_{11} & q_{12} & q_{13} \\ q_{12} & q_{22} & q_{23} \\ q_{13} & q_{23} & q_{33} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}x \\ y \\ z\end{bmatrix} = - \begin{bmatrix}q_{14} \\ q_{24} \\ q_{34}\end{bmatrix}\)
- 有时候矩阵不可逆(奇异)
- 直接使用 v1 或 v2
- 使用边中点 \((v_1+v_2)/2\)
- 选择并折叠边
- 选择误差最小的边折叠为 \(v_{\text{new}}\)
- 更新邻接面的顶点索引
- 删除退化三角形 → 面积为 0 的三角形
- 更新 Quadric 和优先队列
- \[Q_{v_{\text{new}}} = Q_{v_1} + Q_{v_2}\]
- 更新相关边的误差和优先队列
- 重复步骤 3–4,直到满足目标三角形数量或误差阈值
其他
Edge Collapse, Vertex Clustering, Surface Simplification
Triangle Soup
没有拓扑;面之间也可能不连通;无法正确计算折叠误差
- 它不是“坏掉的网格”,而是一种不完整或未连接的几何近似。
- 可能由扫描噪声、重建误差、布尔运算、或数据格式转换引起
Vertex Clustering / Cell Collapse
- 空间划分(Spatial Partitioning)
- 确定模型的包围盒(bounding box);
- 将空间划分成均匀立方体格子(voxels / cells);
- 每个 cell 的边长 = 预设的聚类尺寸(例如模型尺度的 1%);
- 每个三角形的顶点根据坐标落入某个 cell。
- 顶点合并(Vertex Merging): 对每个 cell:
- 收集其中所有的顶点;
- 计算它们的代表点(representative vertex),通常是:
- 所有顶点的平均位置(centroid),或
- 体素中心,或
- 第一个顶点的位置(快速版本)
- 三角形重建(Triangle Remapping)对于原始三角形:
- 将其三个顶点分别替换为它们所在 cell 的代表点;
- 如果三个点最终落在同一个 cell(即合并成一个点),这个三角形被删除;
- 否则,用新顶点生成一个新三角形。
- 去重与清理(Post-Processing)
- 去掉重复三角形;
- 可选:去掉退化三角形(面积为0);
- 输出最终简化后的 mesh。
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: